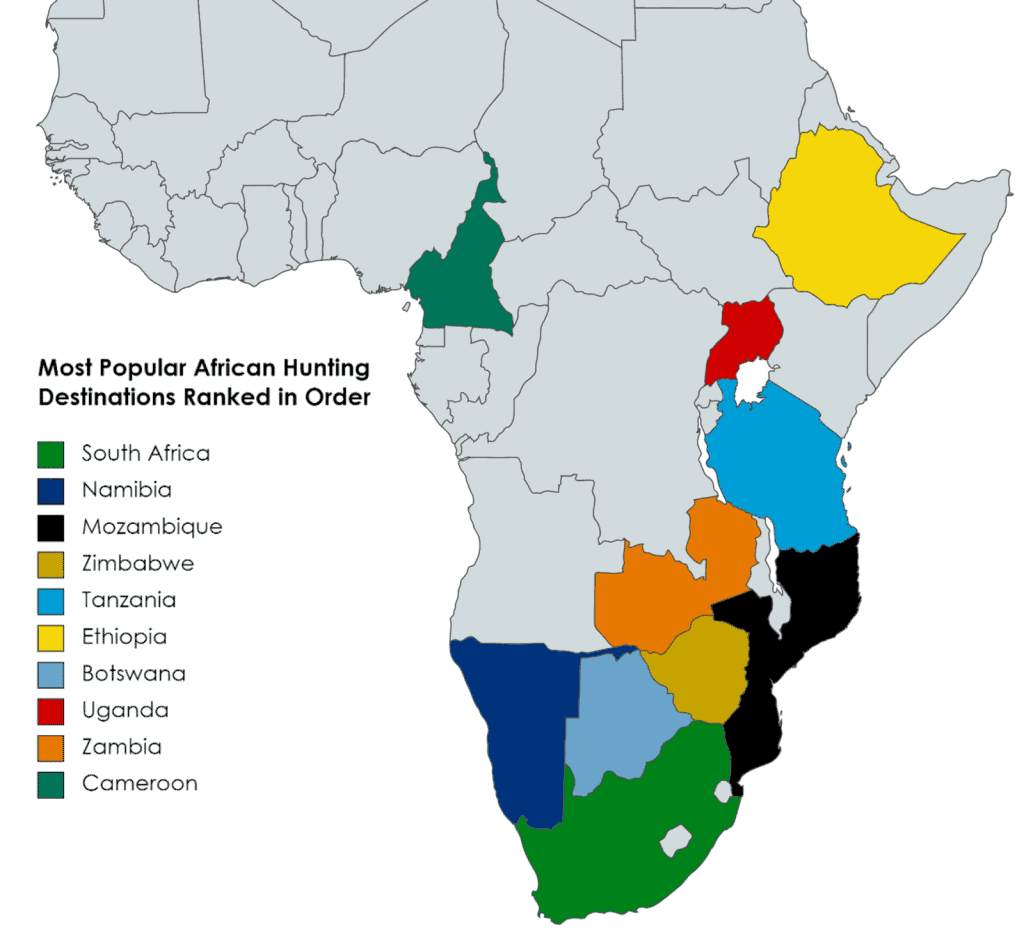
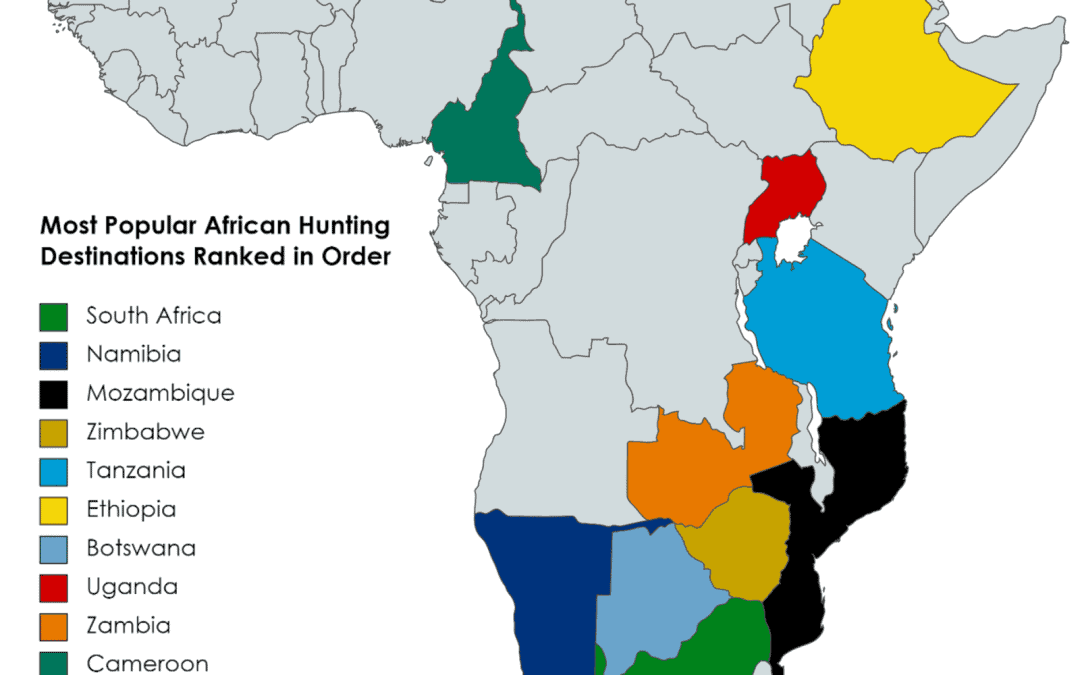
Picture this: you’re deep in the wild, heart thumping in anticipation, as you track your prey through the dense African savannah. The sun beats down on your back, intensifying the exhilaration and intensity of the hunt. But amidst this thrilling adventure, it’s vital to acknowledge the potential dangers lurking in the African wilderness. From encounters with dangerous predators to the risk of contracting tropical diseases, hunting in Africa poses unique challenges that set it apart from other regions. In this article, we’ll explore the specific dangers faced by hunters in Africa, shedding light on the distinct risks that make it a true adrenaline-fueled expedition.
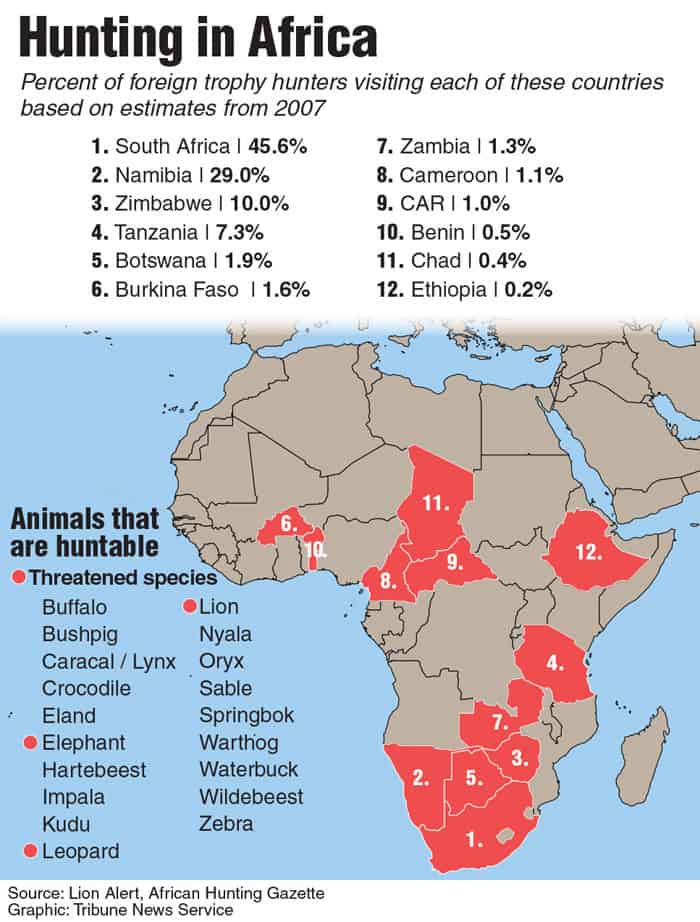
Political Instability and Civil Unrest
Potential for armed conflicts
When it comes to hunting in Africa, one of the major concerns is the potential for armed conflicts. Many countries in Africa have a history of political instability, and these unstable conditions can create an environment where armed conflicts are more likely to occur. This can pose a serious risk to hunters, as they may find themselves in the midst of violence and unrest.
Risks associated with political instability
Political instability also brings about a range of risks. Governments may be weak or corrupt, leading to a lack of law enforcement and regulation. This can create a hazardous environment for hunters, as there may be limited oversight and accountability for their actions. Additionally, political unrest can create tensions between different groups or communities, further increasing the risk of violence and conflict.
Lack of law enforcement
In regions with political instability, the lack of law enforcement can be a significant concern. Without proper regulation and enforcement, hunters may engage in unsafe and unethical practices with little or no consequences. This not only poses a risk to the hunters themselves but also to the wildlife populations and local communities who depend on these resources. Without proper law enforcement, it can be challenging to ensure sustainable hunting practices and protect endangered species.
Inadequate Safety Regulations
Lax regulations on hunting practices
Another danger of hunting in Africa compared to other regions is the lax regulations on hunting practices. In some areas, hunting regulations may be minimal or poorly enforced, allowing hunters to engage in unsafe and unsustainable practices. This lack of oversight can pose risks to both hunters and wildlife, as it may lead to overhunting, habitat destruction, and the spread of diseases.
Limited oversight and accountability
In addition to lax regulations, there may also be limited oversight and accountability for hunting practices. Poor governance and corruption can hinder effective monitoring and enforcement of hunting regulations. Without proper oversight, it becomes difficult to ensure that hunters are acting responsibly and ethically, increasing the likelihood of negative impacts on wildlife populations and their habitats.
Unsafe hunting practices
The lack of adequate safety regulations in some African countries can also result in unsafe hunting practices. Without proper training and guidance, hunters may be ill-prepared to handle potential dangers and emergencies that may arise during their hunts. This can include mishandling firearms, lack of knowledge about local wildlife behavior, and failure to take necessary precautions. Such unsafe practices can lead to accidents, injuries, and even fatalities among hunters and guides.
Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade
Increase in poaching activities
Africa has seen a significant increase in poaching activities in recent years, posing a considerable danger to hunters. Poaching, the illegal hunting and capturing of wildlife, is driven by the high demand for African wildlife products such as ivory, rhino horn, and exotic animal parts. Hunters who visit Africa may inadvertently find themselves encountering poachers or operating in areas that have been heavily impacted by poaching.
High demand for African wildlife products
The high demand for African wildlife products, particularly in international markets, fuels the illegal wildlife trade. This demand puts additional pressure on already threatened species and their habitats. For hunters, the presence of poachers increases the risk of dangerous encounters, as these individuals may go to great lengths to protect their illegal activities.
Potential encounters with poachers
The presence of poachers in hunting areas creates a range of potential dangers. Poachers often operate under the cover of darkness and may be armed, making encounters with them highly unpredictable and hazardous. Hunters and their guides need to be aware of the risks and take necessary precautions to avoid or handle such encounters to ensure their safety.
Wildlife Disease and Health Risks
Prevalence of zoonotic diseases
Hunting in Africa can expose hunters and local communities to various wildlife diseases, including zoonotic diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans. Africa is known for its rich biodiversity and hosts a wide array of viruses, parasites, and bacteria that pose potential health risks. Diseases such as Ebola, anthrax, and tuberculosis have been linked to wildlife in Africa, and hunters need to be mindful of the potential exposure to these diseases.
Viruses, parasites, and bacteria
Wildlife in Africa can carry a host of viruses, parasites, and bacteria, some of which may be harmful to humans. These pathogens can be transmitted through direct contact with wildlife, consumption of contaminated meat, or exposure to infected bodily fluids or waste. Hunters should be cautious when handling the animals they kill, as well as while consuming the meat or utilizing any animal byproducts.
Transmission risks to hunters and local communities
The transmission of wildlife diseases poses risks not only to hunters but also to local communities living in close proximity to hunting areas. Lack of proper medical facilities and healthcare infrastructure in remote areas can further exacerbate the risks and difficulties in managing or treating diseases. It is crucial for hunters to take appropriate preventative measures, such as wearing protective clothing and ensuring a safe and hygienic handling of hunted animals.
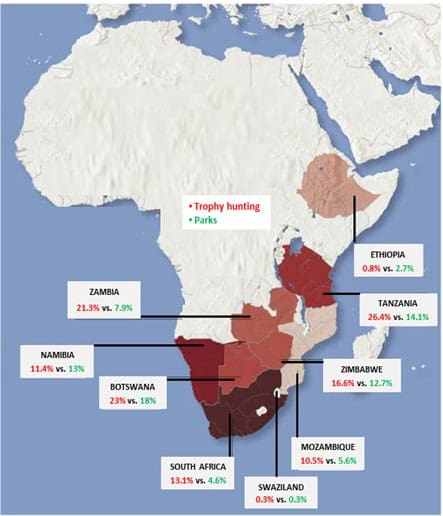
Dangerous and Aggressive Animal Species
Large predators and herbivores
When hunting in Africa, hunters must consider the presence of large predators and herbivores. The African continent is home to iconic and potentially dangerous species such as lions, leopards, elephants, and Cape buffalo. These animals have the strength, speed, and aggression to cause significant harm or even fatalities if a hunter finds themselves in a close encounter or a dangerous interaction.
Potential for close encounters
Africa’s diverse wildlife habitats can bring humans into close proximity with potentially dangerous animals while hunting. Whether it’s tracking or stalking prey, hunters may unknowingly find themselves in close encounters with large carnivores or herbivores. Such interactions can escalate quickly, especially if the animals feel threatened or cornered, leading to potentially life-threatening situations.
Increased likelihood of dangerous interactions
Compared to hunting in other regions, the proximity to dangerous and aggressive animal species is significantly higher in Africa. Hunters must be well-prepared and knowledgeable about the behavior and habitats of the species they are targeting. It is crucial to follow safety guidelines, rely on experienced guides, and exercise caution to mitigate the risks associated with encountering and hunting these animals.
Challenging Terrain and Weather Conditions
Vast and diverse landscapes
Africa is known for its vast and diverse landscapes, ranging from dense forests to open savannahs to mountainous regions. These varied terrains often present hunters with unique challenges, such as navigating through dense vegetation, traversing rugged terrain, or dealing with extreme temperature fluctuations. The vastness and complexity of African landscapes can make hunting a physically demanding and mentally exhausting endeavor.
Navigational difficulties
Navigating through unfamiliar terrains poses a considerable risk for hunters in Africa. Thick vegetation, lack of clear landmarks, and unmarked trails can easily lead to disorientation and loss of direction. Hunters must have exceptional navigational skills or rely on experienced guides who are familiar with the local terrain to ensure their safety and prevent getting lost or stranded in remote and unfamiliar areas.
Extreme weather patterns
Africa experiences a wide range of extreme weather patterns, including intense heat, heavy rainfall, and droughts. These weather conditions can have a significant impact on hunting activities, increasing the risks associated with venturing into the wilderness. Exposure to extreme heat can lead to dehydration and heatstroke, while sudden downpours can make terrains slippery and dangerous. Hunters need to be aware of the weather forecast and take appropriate precautions to ensure their safety in changing weather conditions.
Limited Medical Facilities and Emergency Services
Remote hunting areas
Hunting expeditions in Africa often take place in remote areas that may have limited access to medical facilities and emergency services. Hunters, especially those venturing deep into the wilderness, may find themselves far away from any form of immediate medical assistance. In case of an accident or a medical emergency, the lack of nearby medical facilities can lead to delays in receiving the necessary care, potentially exacerbating the severity of injuries or health conditions.
Lack of immediate medical assistance
Even in areas with a semblance of healthcare infrastructure, the availability of immediate medical assistance can still be a concern. Medical facilities in remote regions may have limited resources, including medical personnel, equipment, and medication. This can make it challenging to receive prompt and adequate medical attention, particularly for serious or life-threatening injuries that may occur during hunting expeditions.
Delays in emergency response
Due to the remote nature of many hunting areas in Africa, emergency response times can also be significantly delayed. In case of serious accidents or emergencies, it may take considerable time for help to arrive, further highlighting the importance of preparedness and preventative measures. Hunters should be equipped with basic first aid knowledge and supplies to manage any injuries or health issues until professional medical help can be accessed.
Firearm Safety and Accidents
Inadequate firearm training
Firearm safety is a critical aspect of hunting, and inadequate training in Africa compared to other regions can pose additional risks. The use of firearms requires proper knowledge and skills to handle them safely and responsibly. Insufficient firearm training can lead to accidental discharges, mishandling of firearms, or failure to follow safety protocols, increasing the likelihood of injuries to both hunters and guides.
Risk of accidental discharges
Accidental discharges of firearms during hunting expeditions can have severe consequences. Mishandling or improper storage of weapons can result in unintentional firing, causing injuries to the hunter, guides, or even bystanders. Hunters must adhere to strict safety guidelines, such as keeping their fingers off the trigger until ready to shoot, maintaining control over their firearms, and never pointing them at anything they do not intend to shoot.
Potential injuries to hunters and guides
Failure to follow firearm safety protocols can lead to injuries for both hunters and guides. Accidental discharges, negligent handling, or the misuse of firearms can result in severe wounds, loss of limbs, or even fatalities. Prioritizing comprehensive training in firearm safety, coupled with regular practice and awareness, is vital to mitigate the risks associated with handling firearms during hunting expeditions.

Travel Risks and Security Concerns
Safety risks during travel
Traveling to and within Africa for hunting purposes can bring about additional safety risks. Depending on the destination and routes taken, there may be safety concerns related to road conditions, transportation modes, or the general security environment. It is crucial to research and stay updated on travel advisories and ensure that necessary precautions are taken to minimize the risks involved.
Threats of robbery and kidnapping
In certain regions of Africa, the risk of robbery or kidnapping cannot be ignored. Tourists, including hunters, may be targeted by criminal elements seeking ransom or valuables. It is important to be cautious, follow local security protocols, and, if possible, hire reputable guides or security personnel who are well-versed in the specific risks of the area. Maintaining good situational awareness and avoiding known high-risk areas is crucial for personal safety.
Insufficient travel advisories
While travel advisories provide valuable information on safety and security, there may be instances where insufficient or outdated advisories exist for certain regions in Africa. It is essential for hunters to conduct thorough research, consult with local authorities, and engage reputable travel agencies or local contacts who can provide accurate and up-to-date information on potential risks and safety precautions.
Ethical Considerations and Conservation Impact
Debate surrounding trophy hunting
Hunting in Africa is a topic of debate due to ethical considerations and its impact on conservation efforts. Trophy hunting, where animals are legally hunted primarily for their body parts or trophies, has been controversial and faced criticism from various animal rights and conservation organizations. While some argue that regulated hunting can contribute to conservation funding and sustainable land and wildlife management, others assert that it poses a threat to endangered species and perpetuates unethical practices.
Impact on endangered species
The hunting industry in Africa, if not properly regulated, can have negative impacts on endangered species. Unsustainable hunting practices, targeting protected or threatened species, or hunting in areas where populations are already under pressure can further jeopardize their survival. Balancing the potential economic benefits of hunting with the need to preserve biodiversity is crucial to mitigate the impact on endangered species and ensure long-term conservation efforts.
Socio-cultural implications
Hunting in Africa also has socio-cultural implications, as it intersects with local communities and their traditions. Indigenous communities often have longstanding relationships with wildlife and ecosystems, practicing sustainable hunting methods embedded in their cultural heritage. However, when hunting practices are exploited for commercial gain or disregarded in favor of trophy hunting, it can lead to the erosion of cultural practices and disrupt the delicate balance between communities and their natural surroundings.
In conclusion, hunting in Africa poses unique and specific dangers compared to other regions around the world. Political instability, inadequate safety regulations, the prevalence of poaching, the risk of wildlife diseases, encounters with dangerous animals, challenging terrains and weather conditions, limited medical facilities, firearm safety concerns, travel risks, and ethical considerations all contribute to the potential hazards associated with hunting in Africa. Is it crucial for hunters to be well-informed, prepared, and take necessary precautions to ensure their safety, promote sustainable hunting practices, and contribute to the conservation of Africa’s rich biodiversity.